Solar Thermal vs Solar PV: What’s the Real Difference?

As the world shifts towards renewable energy, solar power stands out as a leading option. Among the various solar technologies, solar thermal and solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are two prominent choices. While they both harness energy from the sun, they operate differently and serve different purposes. This article breaks down the differences between solar thermal and solar PV to help you decide which might be the best fit for your needs. Key Takeaways Introduction to Solar Energy Technologies I’ve been following the solar energy scene for a while now, and it’s amazing how much things have changed. We’re not just talking about those old-school solar panels anymore. There are so many different ways to grab energy from the sun, and it’s becoming a bigger part of our lives. Solar energy is radiant energy emitted by the sun. Think about it: from heating our homes to powering entire cities, the sun’s energy is becoming more accessible and affordable. It’s a really exciting time to see how these technologies are evolving and how they’re helping us move towards a more sustainable future. I’m going to break down two of the main ways we use solar energy: solar thermal and solar photovoltaic (PV). Both are cool, but they work in totally different ways. Understanding the basics is key if you’re thinking about concerns about climate change or just want to know more about where our energy comes from. Solar energy is becoming more and more important as we look for ways to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. It’s not just about being green; it’s also about creating a more secure and stable energy supply for the future. Here’s a quick rundown of why solar energy is such a big deal: And here’s a little table to show how much solar capacity has grown over the years: Year Solar Capacity (GW) 2010 15 2020 714 2024 >1,000 It’s pretty clear that solar is here to stay, and I’m excited to solar PV and solar thermal technologies in more detail. What is Solar Thermal Energy? Solar thermal energy is all about using the sun’s energy to create heat. Instead of making electricity directly, like solar PV, it heats up a fluid that we can then use for various purposes. It’s a pretty neat way to harness the sun’s power, and it’s been around for a while. I think it’s a technology that’s often overlooked, but it has some serious potential. How Solar Thermal Systems Work So, how does this whole solar thermal thing actually work? Well, it starts with collectors. These collectors are designed to absorb sunlight and transfer that energy into a fluid, usually water or a special heat-transfer fluid. The heated fluid can then be used directly for things like heating water or air, or it can be stored for later use. There are different types of collectors, each suited for different temperature ranges and applications. For example, molten salt thermal energy storage can be used to store heat for later use. Applications of Solar Thermal Energy Solar thermal energy has a bunch of different uses, which is pretty cool. Here are a few examples: Solar thermal systems are an efficient and environmentally friendly method for residential or commercial heating. They reduce the user’s dependency on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. What is Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Energy? Okay, so let’s talk about solar photovoltaic (PV) energy. I think it’s pretty cool how we can grab sunlight and turn it directly into electricity. It’s not magic, but it sure feels like it sometimes. Basically, solar PV is a system that uses solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. These panels are made up of photovoltaic cells, which are also called solar cells. These cells use something called the photovoltaic effect to turn light into electricity. How Solar PV Systems Work So, how does this whole thing work? Well, photovoltaic panels are made of semiconductor materials, usually silicon. When sunlight hits the panel, the semiconductor absorbs energy from the photons in the light. This energy knocks electrons loose from their atoms, creating a flow of electrons. This flow is what we call an electric current. The current is direct current (DC), so we use an inverter to change it into alternating current (AC), which is what most of our appliances use. It’s a pretty neat process, if you ask me. Solar PV systems are pretty straightforward. Sunlight hits the panel, electrons get excited, and electricity is produced. The inverter then makes sure that electricity is usable in your home. It’s a clean and efficient way to generate power. Applications of Solar PV Energy Solar PV energy has a ton of uses. Here are a few: Key Differences Between Solar Thermal and Solar PV Efficiency Comparison When it comes to efficiency, solar PV and solar thermal operate in different ways, making a direct comparison a bit tricky. Solar PV’s efficiency is measured by how well it converts sunlight directly into electricity, and this is improving all the time. Solar thermal, on the other hand, focuses on capturing heat, and its efficiency depends on how well it can transfer that heat for use. I’ve found that PV systems are generally more versatile because electricity can be used for almost anything, while thermal systems are more specialized for heating applications. It’s worth noting that solar thermal systems can be less efficient in winter due to weaker sunlight. Cost Analysis of Solar Thermal vs Solar PV Cost is a big factor for most people considering solar energy. Here’s a quick rundown: From my research, I’ve learned that the cost-effectiveness of each system depends heavily on the specific application and location. For example, if you primarily need hot water, a well-designed solar thermal system might be more cost-effective. However, if you need electricity, PV is the clear winner. Ultimately, it’s about what you need the energy for. Environmental Impact of Solar Technologies It’s easy to think of solar energy as purely green, but like any technology,
What is Solar Energy and How Does it Works

Solar energy is a powerful and renewable resource that harnesses sunlight to generate electricity and heat. This energy source is becoming increasingly popular as people look for cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels. In this article, we’ll break down what solar energy is, its history, how it works, and the different types of solar energy systems available today. We’ll also explore the benefits of going solar and what the future holds for this sustainable energy source. Key Takeaways What Is Solar Energy? So, what exactly is solar energy? Well, in simple terms, it’s energy that comes from the sun. This energy is harnessed in a few different ways to provide heat, electricity, and even power for cooking. It’s a pretty big deal because it’s a renewable resource, meaning we’re not going to run out of it anytime soon (like, for another five billion years or so). Solar energy can be used in a variety of ways. For example: Solar energy is a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. It reduces our reliance on non-renewable resources and helps to lower our carbon footprint. Plus, it’s becoming more affordable and accessible all the time, making it a viable option for more and more people. There are two main types of solar energy technologies: Solar energy is practical in areas with high amounts of sunlight and low cloud cover. Homes and businesses that install solar panels can even produce excess electricity and sell it back to the power grid, which can reduce or even eliminate power bills. When Was Solar Power Discovered? It’s interesting to think about how long we’ve known about solar power. It wasn’t some recent invention; the basic science goes way back. The story starts with some pretty cool discoveries that laid the groundwork for everything we use today. The real breakthrough came in 1839 when Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, a French physicist, discovered the photovoltaic effect. Basically, he found out that you could generate electricity by exposing certain materials to light. He was just 19 years old when he made this discovery! Becquerel’s experiment involved silver-chloride in an acidic solution. When he shined light on it, platinum electrodes attached to the solution generated an electric current. This was the first time someone had observed electricity being produced directly from sunlight, and it’s the foundation of how solar panels work today. It’s amazing to think that a teenager’s experiment from almost two centuries ago is still relevant today. Becquerel’s discovery wasn’t immediately put to practical use, but it opened the door for future scientists and engineers to develop the solar technologies we rely on now. While Becquerel’s discovery was a major step, it took many years for the technology to develop into something useful. It wasn’t until the 20th century that solar cells became efficient enough to be practical. Still, his work is the starting point for understanding how we harness solar energy today. Here’s a quick timeline: Is Solar Energy Renewable? So, is solar energy renewable? Absolutely! Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source because it comes from the sun, which is pretty much an endless supply of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form and are finite, the sun will keep shining for billions of years. That’s a long time! Think about it this way: Switching to renewable energy sources like solar is a big step towards a more sustainable future. It means less pollution, less environmental damage, and a more secure energy supply for everyone. One of the coolest things about solar is that it’s clean. Once the solar panels are up and running, they don’t produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This is a huge contrast to burning fossil fuels, which release all sorts of nasty stuff into the atmosphere. Plus, homes and businesses that install solar panels can even sell excess electricity back to the electric provider, reducing or even eliminating power bills. How Does Solar Energy Work? Solar energy is captured and converted into usable forms through various methods. These methods generally fall into two categories: active and passive. Active solar technologies use electrical or mechanical devices to convert solar energy, while passive technologies leverage the local climate to heat or cool structures without external devices. How Do Solar Panels Work? Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) modules, are the most common way to harness solar energy. They’re made up of numerous solar cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. Each cell contains a semiconductor material, usually silicon. When sunlight strikes the cell, it knocks electrons loose from the silicon atoms. These electrons are then forced to flow in one direction, creating an electric current. Metal contacts on the top and bottom of the cell collect this current, which can then be used to power electrical devices or sent to the grid. This process is called the photovoltaic effect. How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity? The process of generating electricity with solar panels involves several key steps: Solar panels are pretty amazing when you think about it. They quietly sit on your roof, soaking up the sun and turning it into electricity with no moving parts. It’s a clean, reliable way to generate power, and it’s becoming more and more affordable all the time. How Does a Solar Panel System Work? A complete solar panel system involves more than just the panels themselves. It includes several other components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electricity. Here’s a breakdown of how a typical system works: What Does a Solar Inverter Do? The solar inverter is a critical component of any solar panel system. Its primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the standard form of electricity used in most homes and businesses. Without an inverter, the electricity generated by solar panels would not be compatible with most appliances and electrical devices. Inverters also perform other important functions, such as monitoring the system’s
How to Calculate Your Home’s Solar Energy Needs
When considering how to calculate your home’s solar energy needs, understanding your current energy consumption is pivotal. By analyzing your utility bills, you can pinpoint your average daily electricity usage and make informed decisions about solar panel sizing. However, this is just the starting point. To ensure an accurate assessment tailored to your specific requirements, there are additional factors to consider. From peak sun hours to system efficiency, each element plays a crucial role in determining the optimal solar energy solution for your home. Learn About Costs and FinancingUnderstand the investment and financing options for solar energy.🔗 Get Details Key Takeaways Assess Your Energy Consumption When assessing your energy consumption for calculating solar energy needs, the first step is to gather all your utility bills from the past year. Take a look at the total kilowatt-hours (kWh) used each month. This data will provide you with a clear picture of your average energy usage throughout the year. Next, identify any significant changes in your energy consumption patterns. Did you install new appliances, change your heating or cooling systems, or implement energy-saving practices? These factors can impact the amount of solar energy your system will need to produce. Additionally, consider any future changes you might make that could affect your energy usage. Understanding your current energy consumption is crucial for accurately determining the size and capacity of the solar energy system that will best suit your needs. Determine Your Peak Sun Hours To accurately determine your solar energy needs, it’s essential to understand the concept of peak sun hours. Peak sun hours refer to the number of hours in a day when the sun produces enough sunlight for solar panels to operate at their maximum efficiency. This is crucial for calculating how much solar energy your home can generate and how many solar panels you need. Peak sun hours vary depending on factors like your location, the season, and any shading that may affect your solar panels. Areas closer to the equator typically have more peak sun hours compared to regions further away. By determining the average peak sun hours for your location, you can estimate the amount of energy your solar panels will produce each day. Knowing your peak sun hours is vital for sizing your solar energy system correctly. It ensures that you install a system that can generate enough electricity to meet your home’s energy demands efficiently. Calculate Your Daily Energy Usage Determining your daily energy usage is a crucial step in accurately sizing your solar energy system for your home. To calculate your daily energy needs, start by examining your utility bills to understand your average daily consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Take note of seasonal variations in energy usage as well. Additionally, consider any major appliances or devices you plan to power using solar energy and estimate their daily energy consumption. It’s important to factor in any future changes in your energy usage, such as adding new appliances or electric vehicles. By understanding your daily energy needs, you can determine the size of the solar energy system required to meet your household’s electricity demands. This information will help you choose the appropriate solar panel capacity and battery storage, ensuring that your system can generate enough energy to power your home efficiently. Taking the time to accurately calculate your daily energy usage will set you on the right path towards a successful solar energy installation. Consider Energy Efficiency Measures Considering energy efficiency measures is essential when planning for your solar energy system. By improving your home’s energy efficiency, you can reduce the overall energy consumption and size requirements of your solar panel system. This not only saves you money on the initial installation but also on your long-term energy bills. Simple changes like upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and sealing drafts can make a significant impact on your energy usage. To illustrate the potential impact of energy efficiency measures, consider the table below: Energy Efficiency Measure Estimated Energy Savings (%) Cost ($) LED Lighting Upgrade 75 500 Smart Thermostat Install 15 250 Insulation Improvement 20 1000 Energy Star Appliances 30 2000 Window Upgrades 10 1500 These measures not only reduce your energy consumption but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly lifestyle. Factor in System Losses Improving your home’s energy efficiency is just the beginning of optimizing your solar energy system. When calculating your home’s solar energy needs, it’s crucial to factor in system losses. System losses refer to the energy that’s lost as your solar power travels from the panels to your appliances due to various inefficiencies in the system. Several factors contribute to system losses, including shading from nearby buildings or trees, dust accumulation on the solar panels, voltage drops in the wiring, and inverter inefficiencies. These losses can significantly impact the overall performance of your solar energy system, reducing the amount of usable energy that reaches your home. To account for system losses accurately, it’s essential to work with a solar energy professional who can conduct a detailed assessment of your property and design a system that minimizes these losses. Size Your Solar Panel Array To properly size your solar panel array, you need to calculate the total energy consumption of your home and determine how much of that energy can be offset by solar power. Here are some key points to consider: Account for Seasonal Variations Now that you have sized your solar panel array to meet your energy needs, it’s important to factor in seasonal variations when planning for optimal energy production. Seasonal changes can significantly impact the amount of sunlight your solar panels receive, affecting their efficiency and overall energy output. To account for these variations, it’s crucial to understand how the angle of the sun and daylight hours change throughout the year in your specific location. Consider the following factors when calculating your home’s solar energy needs across different seasons: Season Sunlight Hours Sun Angle Summer Long High Fall Moderate Moderate Winter Short Low Spring Increasing Increasing
The Evolution of Solar Technology: Past, Present, and Future
As you explore the evolution of solar technology, you’ll find a fascinating journey from ancient methods to cutting-edge innovations. The progression from simple solar heating techniques to sophisticated photovoltaic systems has revolutionised how we harness sunlight for energy. But what lies ahead in the realm of solar technology? The possibilities for further advancements seem endless, with ongoing research and development paving the way for a future where solar power could play an even more prominent role in our quest for sustainable energy solutions. Key Takeaways Origins of Solar Technology From ancient civilisations to modern innovations, the origins of solar technology trace back through centuries of human ingenuity and curiosity. T The fascination with harnessing the power of the sun dates back to as early as the 7th century B.C., when magnifying glasses were used to concentrate sunlight and start fires. 🔆 Solar Myth Debunked Solar panels don’t only work in sunny states! Even regions with frequent clouds can benefit from solar energy. Learn more in our article: Solar Energy Myths Debunked. Fast forward to the 3rd century B.C., and the Greeks and Romans were utilising mirrors to light torches for religious ceremonies. The concept of solar power continued to evolve, with the first solar collector invented in 1767 by Swiss scientist Horace-Bénédict de Saussure. This insulated box, known as the “hot box,” could reach temperatures of 230 degrees Fahrenheit by trapping solar heat. As time progressed, so did solar technology. In the 19th century, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, laying the foundation for modern solar panels. Early Innovations and Applications Early innovations in solar technology paved the way for practical applications that showcased the potential of harnessing the sun’s energy. One significant development was the invention of solar water heaters in the late 19th century, which utilised sunlight to heat water for domestic use. This marked a crucial step towards utilising solar energy for everyday needs. Additionally, in the 1950s, the first solar cells were created, converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. These early solar cells were primarily used in space exploration, powering satellites and spacecraft. During the 1970s energy crisis, solar technology gained momentum as a viable alternative to traditional energy sources. Solar panels began to appear on rooftops and in remote locations where traditional power sources were impractical. These early applications demonstrated the versatility and reliability of solar energy. As research continued, advancements in solar technology led to improved efficiency and affordability, setting the stage for the modern solar revolution that continues to evolve today. Modern Solar Technologies In recent years, advancements in solar technology have propelled the industry forward at a rapid pace. Modern solar technologies have made significant strides in efficiency and accessibility. One of the key developments is the improvement in photovoltaic (PV) cell efficiency, allowing for better conversion of sunlight into electricity. These advances have led to sleeker and more powerful solar panels that can generate more energy in less space. Moreover, the integration of smart technology and monitoring systems has revolutionized the way we interact with solar energy. Homeowners can now track their energy production in real-time, optimize consumption patterns, and even sell excess energy back to the grid. In addition, energy storage solutions like lithium-ion batteries have become more affordable and efficient, enabling households to store excess energy for use during peak hours or when sunlight isn’t available. Advancements in Efficiency and Affordability Solar technology has seen remarkable progress in recent years, particularly in enhancing efficiency and driving down costs. These advancements have made solar energy more accessible and attractive to a wider audience. Here are three key developments contributing to the increased efficiency and affordability of solar technology: Emerging Trends and Technologies Pioneering innovative technologies are reshaping the landscape of renewable energy, propelling the solar industry towards new horizons. One emerging trend is the integration of solar power with energy storage solutions, such as advanced batteries. This development allows for better utilisation of solar energy by storing excess power for later use, even when the sun isn’t shining. 🔆 Solar Tip for Businesses Small businesses can save money and boost sustainability by investing in solar energy. Discover how it can benefit your business in our article: Why Small Businesses Should Invest in Solar Energy. Additionally, the rise of smart solar technologies, like microinverters and power optimisers, is enhancing system performance by maximising energy production at the individual solar panel level. Another significant advancement is the increased adoption of bifacial solar panels, which can capture sunlight from both the front and back sides, boosting overall efficiency. Moreover, the use of perovskite solar cells shows promise for higher efficiency rates and lower production costs. These cells can be integrated into various surfaces, expanding the possibilities for solar energy generation. The Future of Solar Energy The horizon of solar energy is brimming with exciting possibilities as technological advancements continue to drive the industry forward. As you look ahead to the future of solar energy, here are three key trends to keep an eye on: Increased Efficiency: Innovations in solar panel design and materials are enhancing efficiency levels, allowing for more energy production from the same amount of sunlight. This increased efficiency not only improves the overall performance of solar systems but also makes them more cost-effective for consumers. Energy Storage Solutions: The development of better energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries and grid-scale storage systems, is poised to revolutionise the solar energy sector. These solutions will enable solar power to be available even when the sun isn’t shining, ensuring a more reliable and stable energy supply. Smart Integration and Digitalisation: The integration of smart technologies and digital solutions into solar energy systems is paving the way for improved monitoring, control, and optimization of solar installations. This trend towards smart integration enhances system performance, increases flexibility, and ultimately makes solar energy more accessible and user-friendly. Frequently Asked Questions Can Solar Technology Work in Areas With Limited Sunlight? Yes, solar technology can work in areas with limited sunlight. While
Understanding Solar Power vs. Traditional Energy Sources

When considering the transition towards sustainable energy sources, it’s crucial to grasp the nuances between solar power and traditional energy methods. The benefits and drawbacks of each play a pivotal role in shaping our energy landscape. By unraveling the complexities of solar power versus conventional energy sources, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the implications for our environment and economy. Key Takeaways Solar Power Basics When it comes to understanding solar power basics, one key concept to grasp is how sunlight is converted into electricity. Solar panels, made up of photovoltaic cells, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. These cells are typically made of silicon, a semiconductor material that releases electrons when exposed to sunlight. The flow of these electrons creates an electrical current, which can then be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity using an inverter. This AC electricity can power homes, businesses, and even entire communities, providing a sustainable and renewable energy source that helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Traditional Energy Sources Overview Exploring traditional energy sources reveals a diverse mix of non-renewable options like coal, oil, and natural gas that have long powered our modern world. Coal, once a dominant energy source, is known for its abundance and relatively low cost. Oil, crucial for transportation and heating, remains a cornerstone of the global energy mix. Natural gas, cleaner than coal and oil, is increasingly popular for electricity generation. Nuclear energy, generated from uranium, provides a steady power supply with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Hydropower, harnessed from flowing water, is another significant traditional energy source. These sources have been vital for meeting energy demands, but concerns about sustainability and environmental impact drive the search for cleaner alternatives. Environmental Impact Comparison Moving from a focus on traditional energy sources to an examination of their environmental impact sheds light on the implications of our energy choices. Traditional energy sources such as coal and oil release harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and air pollution. In contrast, solar power generates electricity without producing any emissions or pollutants during operation. The production of solar panels does have some environmental impact, primarily in the form of energy consumption and potential chemical waste. However, over the lifetime of a solar system, the environmental benefits far outweigh these initial costs. By choosing solar power over traditional energy sources, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations. Cost Analysis: Solar vs. Traditional Comparing the cost of solar power to traditional energy sources is essential for making informed decisions about energy consumption. Initially, the upfront cost of installing solar panels can be higher, but over time, solar energy proves to be more cost-effective. With advancements in technology, the price of solar panels has significantly decreased, making them more accessible. Moreover, solar energy systems have lower maintenance costs compared to traditional energy sources like coal or natural gas. When considering the long-term benefits and savings on electricity bills, solar power emerges as a more economical choice. It’s crucial to analyze not just the initial investment but also the overall expenses over the system’s lifespan to determine the most cost-effective energy option for your needs. Efficiency and Reliability Factors Analyzing the efficiency and reliability factors of solar power and traditional energy sources is crucial in determining the most suitable energy option for your needs. When comparing these factors, consider the following: Future Outlook and Trends Considering the advancements in technology and the shifting global energy landscape, it’s evident that both solar power and traditional energy sources are experiencing changes that will shape the future of energy production. Solar power is projected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by declining costs of solar panels and batteries, as well as increased efficiency in energy storage solutions. On the other hand, traditional energy sources are also adapting by integrating more renewable energy into their portfolios and exploring cleaner technologies like carbon capture and storage. The future outlook suggests a more diversified energy mix, with solar power playing a significant role in meeting the world’s energy demands while traditional sources evolve to become more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Frequently Asked Questions Can Solar Panels Work in Extreme Weather Conditions? Yes, solar panels can work in extreme weather conditions. They are designed to withstand various elements like snow, hail, and high winds. However, excessive heat can slightly decrease their efficiency, but they still produce power. How Are Traditional Energy Sources Impacting Indigenous Communities? Traditional energy sources are negatively impacting indigenous communities by causing environmental degradation, health issues, and cultural disruptions. You can advocate for sustainable alternatives, support local initiatives, and amplify indigenous voices to address these impacts effectively. Are There Any Health Risks Associated With Solar Power? You should know that while solar power is generally safe, improper installation or maintenance can pose risks like electrical hazards. Regular maintenance and hiring qualified professionals can help ensure your solar system operates safely. What Happens to Solar Panels at the End of Their Lifespan? When solar panels reach the end of their lifespan, they can be recycled to recover materials. This process reduces waste and allows for the reuse of valuable resources. It’s important to properly dispose of them for environmental sustainability. How Do Traditional Energy Sources Contribute to Geopolitical Conflicts? Traditional energy sources, like oil and gas, often lead to geopolitical conflicts due to competition over resources. They can create tensions between nations, impacting global stability. Consider diversifying energy options to reduce reliance on these sources and promote peace. Conclusion In conclusion, choosing solar power over traditional energy sources is a smart and sustainable decision for the future. With zero emissions, decreasing costs, and long-term savings, solar energy offers a cleaner and more efficient alternative. By considering the environmental impact, cost analysis, efficiency, and reliability factors, it’s clear that solar power is a key player in shaping a more sustainable energy landscape. So why wait? Make the switch to
The Basics of Solar Panels How Do They Generate Electricity?
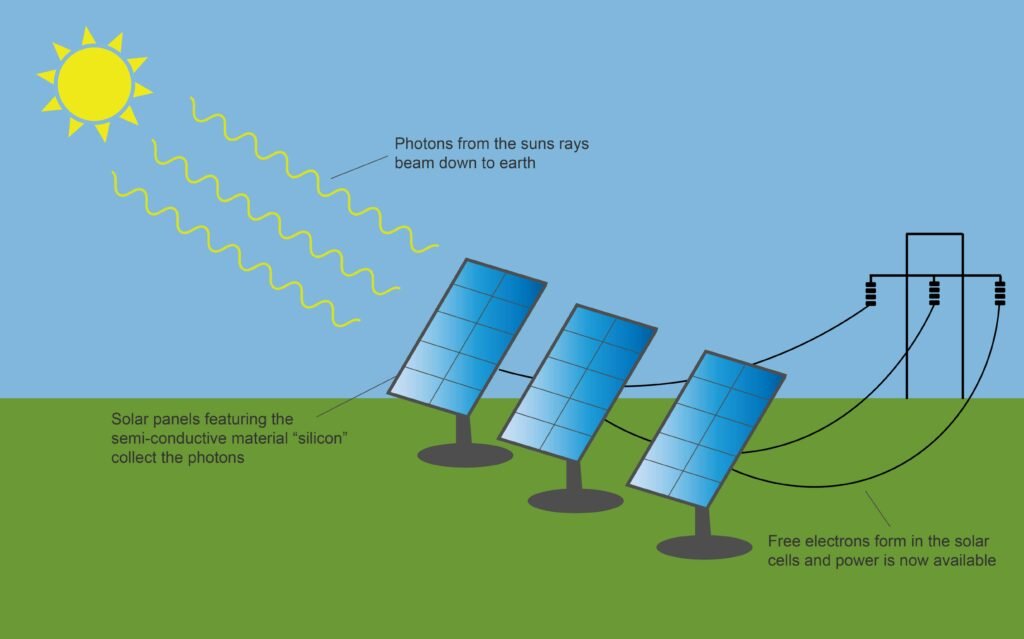
Ever wonder how those shiny panels on rooftops turn sunlight into electricity? It’s not magic, but a clever use of science. Solar panels, often seen glistening under the sun, are more than just a trend—they’re a key player in renewable energy. They take the sun’s rays and convert them into electricity you can use at home. Let’s break down how these panels work and why they’re becoming so popular. Key Takeaways Understanding the Basics of Solar Panels What Are Solar Panels Made Of? Solar panels might look like simple sheets of glass, but there’s a lot more going on beneath the surface. They’re primarily made up of photovoltaic cells, which are usually composed of silicon. These cells are sandwiched between layers of semi-conducting materials that have different electronic properties. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electric field across the layers, sparking the flow of electricity. The panels also include a metal frame and a glass casing to protect the delicate cells from the elements. How Do Solar Panels Capture Sunlight? Capturing sunlight isn’t just about facing the sun. Solar panels are designed to maximize the amount of sunlight they absorb. The photovoltaic cells are grouped into arrays and positioned to capture the most sunlight throughout the day. The angle and orientation of these panels can significantly affect their efficiency. This is why you often see solar panels on rooftops or in open fields, angled perfectly to greet the sun. The Role of Photovoltaic Cells in Solar Panels Photovoltaic cells are the heart of any solar panel. These cells are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the cell, it knocks electrons loose from their atoms. As these electrons flow through the cell, they generate an electrical current. This current is direct current (DC), which needs to be converted to alternating current (AC) for home use. The efficiency of a solar panel largely depends on the quality and type of photovoltaic cells used. How Solar Panels Generate Electricity The Photovoltaic Effect Explained Alright, so let’s dive into how solar panels actually turn sunlight into electricity. The magic begins with the photovoltaic effect. This is when sunlight hits the solar panels, which are made up of photovoltaic cells, usually silicon-based. When these cells catch sunlight, they get all excited and start knocking electrons loose. These free electrons are the ones that create an electric current. It’s pretty wild how sunlight, something we often take for granted, can kickstart this whole process. Converting Sunlight to Direct Current (DC) Once those electrons are free, they move through the cells, creating what’s known as direct current, or DC electricity. This is the raw power that solar panels generate. But here’s the catch: most of our home appliances don’t run on DC. They need alternating current (AC) to function. So, while the panels are busy converting sunlight into DC, there’s another step needed to make it usable in our homes. The Importance of Inverters in Solar Systems This is where inverters come into play. Inverters are crucial because they take the DC electricity from the solar panels and flip it into AC electricity, which is what powers your fridge, TV, and all the other gadgets in your house. Without inverters, the electricity generated by solar panels would just be a bunch of unusable juice. So, when you’re thinking about solar panels, don’t forget about these unsung heroes that make it all work. Solar panels are fascinating because they turn the sun’s rays into a usable form of energy that powers our lives. From the photovoltaic effect to the role of inverters, every step in the process is vital for generating electricity efficiently. Types of Solar Panels and Their Uses Differences Between Solar PV and Solar Thermal Panels When we’re talking about solar panels, it’s important to know that there are two main types: solar photovoltaic (PV) panels and solar thermal panels. The three main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, each with its own unique features. Solar PV panels are all about generating electricity. They use the photovoltaic effect, which basically means they convert sunlight directly into electricity. On the other hand, solar thermal panels are designed to capture the sun’s heat. Solar Tech Explained: Not sure whether solar thermal or solar PV is right for your home? Explore our detailed comparison of solar thermal vs. solar PV to understand differences in cost, efficiency, and applications. They are often used for heating water or air for residential use or even in large-scale power plants. While both types harness the sun’s energy, they serve different purposes and have distinct technologies. Applications of Solar Panels in Homes and Businesses Solar panels are incredibly versatile. In homes, solar PV panels are commonly installed on rooftops to generate electricity, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering energy bills. Businesses also benefit from solar energy by installing panels on large rooftops or unused land to cut operational costs. Some businesses even use solar power as a marketing tool, showcasing their commitment to sustainability. Additionally, solar thermal panels are often used in residential settings for heating water, making them a popular choice for eco-friendly homeowners. The Rise of Solar Farms Solar farms are popping up everywhere, and it’s no surprise why. These large-scale installations are designed to generate electricity for thousands of homes and businesses. They use vast arrays of solar PV panels spread over large areas, often in rural locations. Solar farms are a key player in the push for renewable energy, helping to reduce carbon footprints on a much larger scale than individual installations. Choosing Your Solar Panels? Not sure whether monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels are right for your home? Dive into our comparison of polycrystalline vs. monocrystalline solar panels to learn about efficiency, costs, and long-term benefits. They provide a significant amount of clean energy and are an important part of the transition to a more sustainable energy system. As we move forward, the role of solar
The Benefits Of Installing Solar Panels

Thinking about solar panels? They’re popping up everywhere these days. Not just because they’re eco-friendly, but they can also save you some cash. Imagine reducing your electric bill and maybe even getting some tax breaks. Plus, they’re pretty low maintenance. Sounds good, right? Let’s dive into what makes solar panels a smart choice for many homeowners. Key Takeaways Environmental Advantages of Solar Panels Reduction in Carbon Footprint Switching to solar panels is one of the most effective ways to cut down on our carbon footprint. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which are notorious for releasing harmful carbon emissions into the atmosphere. Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that doesn’t produce greenhouse gases during operation. This means that every kilowatt-hour of solar-generated electricity you use is a step towards a healthier planet. Plus, as more people adopt solar, the cumulative effect can lead to a substantial decrease in overall carbon emissions, helping to combat climate change. Conservation of Water Resources Traditional power generation methods, like coal and natural gas plants, consume vast amounts of water for cooling and other processes. In contrast, solar panels require minimal water to generate electricity. This is a huge advantage, especially in regions where water is scarce. By opting for solar energy, we not only save water but also protect aquatic ecosystems from thermal pollution and other harmful effects of water-intensive energy production. Floating solar panels, which are deployed over water bodies, can even reduce evaporation, conserving water further. Promotion of Energy Independence Solar panels empower us to produce our own electricity, reducing the need to import energy from other regions or countries. This not only enhances national energy security but also decreases the environmental impact associated with transporting fuels over long distances. The ability to generate electricity locally means fewer emissions from transportation and a more stable energy supply. In the long run, widespread solar adoption can lead to a more resilient and self-sufficient energy infrastructure, less vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and supply disruptions. Financial Benefits of Solar Panel Installation Reduction in Electricity Bills Ever opened your electricity bill and thought, “Wow, that’s a bit steep this month”? Well, installing solar panels can help with that. By generating your own electricity, you can significantly cut down on what you pay to the utility company. Imagine slashing your monthly bill by half or even more. It’s not just a dream for some folks; it’s their reality. Depending on where you live and how much sun you get, the savings can be pretty substantial. Eligibility for Tax Credits and Subsidies Now, let’s talk about tax credits and subsidies. When you decide to go solar, Uncle Sam might give you a pat on the back in the form of tax credits. Right now, there’s a federal tax credit that lets you claim 30% of your installation costs. Some states even throw in extra incentives, making it even more tempting. These perks can make a big difference in the overall cost. Increase in Property Value Here’s another cool thing: solar panels can actually boost your home’s value. If you ever decide to sell, potential buyers might be willing to pay more for a house that’s already set up with solar. It’s like having a modern kitchen or a fancy bathroom—it’s an upgrade. And with energy costs always on the rise, a solar-equipped home is a smart investment. Technological Advancements in Solar Energy Efficiency Improvements in Photovoltaic Cells I’ve always been fascinated by how much solar panels have evolved over the years. One of the most exciting advancements is in the efficiency of photovoltaic cells. These cells, which convert sunlight into electricity, have become more efficient, meaning they can generate more power from the same amount of sunlight. It’s like getting more juice out of the same orange. This leap in efficiency is a game-changer for homeowners like me who are looking to maximize energy output while minimizing roof space. Integration with Smart Home Systems Nowadays, solar panels aren’t just standalone units. They’re becoming an integral part of smart home systems. Imagine controlling your solar energy production and consumption right from your smartphone. It’s not just about generating power anymore; it’s about using it smartly. I can adjust my energy usage based on real-time data, which is pretty cool. Plus, integrating solar with smart systems helps in optimizing energy use, leading to even more savings. Development of Solar Battery Storage Solar energy storage has come a long way too. With advancements in battery technology, storing solar power for later use is becoming more feasible and affordable. This means I can store excess energy produced during sunny days and use it when the sun isn’t shining. It’s like having a backup generator without the noise and fumes. Lithium-ion batteries are particularly noteworthy for their efficiency and longevity, ensuring that I can rely on solar power even during cloudy days or at night. Solar technology is not just about harnessing the sun’s energy; it’s about integrating it seamlessly into our lives. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise a future where solar power is not only efficient but also incredibly user-friendly. Impact of Solar Panels on Home Value Increased Resale Value When I first thought about solar panels, I was mostly worried about the cost. But then I learned that homes with solar panels can actually fetch a higher resale price. Buyers are often willing to pay more for a home with solar panels because they see the long-term savings on electricity bills. Some reports even suggest that solar panels can add up to $15,000 to a home’s value. That’s a pretty big deal if you’re thinking about selling your house in the future. Attraction for Eco-Conscious Buyers Let’s face it, more people are becoming eco-conscious these days. This means that homes with solar panels are more attractive to a growing segment of buyers who are looking to reduce their carbon footprint. In a way, having solar panels
The Best Solar Companies for Homeowners in 2025

Discover the top solar companies for homeowners in 2025 and find out which ones offer unbeatable warranties and customer service that could change your energy game.
What to Do Before Installing Solar Panels: A Step-by-Step Guide

Learn essential steps to take before installing solar panels, ensuring you’re prepared for a successful transition to renewable energy. What comes next?
5 Everyday Inverter Problems & How to Solve Them.

The hidden heroes of our homes are inverters. They transform DC power into AC to keep things running. However, they occasionally experience a few glitches, just like any other device. If you don’t know what’s happening, these issues can be annoying. They might be due to voltage problems or blank screens. The good news? The majority of these problems have simple solutions. Let’s examine five typical inverter issues and how to address them directly. 1. The inverter screen is blank. Even though your inverter is configured, the screen seems completely blank. This is rather typical and typically resolvable. Let’s investigate some potential causes of this and find solutions. Examine the DC switch first: You can save a great deal of trouble by taking a moment to check these easy things. Usually, it’s something minor, yet it has a huge impact. If you find problems after your inspections, it may be time to call a pro. However, a little do-it-yourself troubleshooting can typically solve the problem. 2. Overdirect Current Injection Inverter Failure One problem with inverters is failure caused by excessive DC injection. This issue arises when the inverter’s DC detection circuit samples the AC output. It removes the AC component, then compares the DC component to a set value. The inverter signals an error if this value, typically set at 0.5% of the rated current, is exceeded. What is causing this hiccup, then? This kind of failure may result from an abrupt increase in DC input power. It’s similar to when you’re driving and your car skids out of control after you hit a patch of ice. Try these actions to address this: Despite our best efforts, technical problems occasionally necessitate starting over with new tools. It reminds us that, though useful, technology is not perfect. Installing a voltage stabilizer can help protect your inverter. It will ensure steady solar generation if you have frequent voltage issues. 3. Failure of the Bus Voltage Balance The bus voltage balance failure is a subtle problem with inverters. It could surprise you. When half of the BUS+ and BUS- voltages deviate significantly from their halfway voltage, this issue arises. The inverter may indicate a failure as a result of this imbalance, stopping its operation. So, what are your options? Here is a simple checklist to assist you in addressing this problem: The simplest answers might occasionally be the most successful. Many inverter problems may be avoided with early inspections and routine maintenance, which will keep your system operating efficiently. Keep an eye on the inverter’s display in case you run into a “DC Bus Unbalance” issue. Normal operation of the inverter should resume if the voltage levels are balanced. This advice will guarantee that your inverter is operating at its best and save you a great deal of trouble. Study up on DC bus unbalance. 4. An excessively high bus voltage There can be a lot of problems when the bus voltage in an inverter system rises over average. The main issue is that high voltage might damage the inverters or shut them down. Let’s examine how this occurs and what you can do to prevent it. Typical Reasons Solution Tips for Troubleshooting In certain situations, the inverter may have a 13.5A restriction. When solar panels surpass this limit, the inverter will sound a warning and cut the string to avoid harm. To avoid trouble, always ensure your setup meets these requirements. 5. Grid Loss Inverter Failure It can be rather annoying when your inverter abruptly cuts off from the grid. There are remedies; however, this problem typically comes down to a few common causes. Typical Reasons Solution 1. Wait It Out: Often, the best option in a power outage is to wait for the electricity to return. 2. Verify Connections: Check every connection from the grid to the inverter’s AC output. Verify that no breakers are tripped or unsecured wires are present. 3. Modify Voltage Protection Settings: If overvoltage or undervoltage protection is causing problems, you may need to change the settings or seek professional advice to ensure they are suitable for your grid conditions. The biggest headaches can occasionally be caused by the slightest problems. However, with patience and some troubleshooting, you can often get your inverter back online. Final Thoughts Well, people, there you have it. Although inverters might be a little challenging, most problems can be resolved with a little perseverance and basic troubleshooting. Knowing what to check for can save you trouble. It could be a battery that won’t charge or a display that won’t light up. Keep in mind that maintaining your inverter on a regular basis is essential. And don’t be afraid to bring in a professional if everything else fails. It’s better to be safe than sorry, after all. Keep your stress levels down and your power flowing! Commonly Asked Questions Why does nothing appear on the screen of my inverter? First, make sure the DC switch is turned on if the screen of your inverter is blank. If so, there may be a loose connection or a malfunctioning inverter that requires repair. If my inverter is injecting too much direct current, what should I do? This could be the result of an abrupt change in the DC input. Try shutting off the AC/DC switch to restart your inverter. You may need to replace the inverter or update the firmware if the issue persists. How can I resolve my inverter’s bus voltage balance issue? Check that the DC connector is grounded. Also, look for loose wiring in all AC connections. It may be necessary to replace or reconnect any loose internal wiring. How can I resolve an excessively high bus voltage, and what causes it? This can be brought on by an excessive DC input voltage. Verify how many parts are connected in series and, if needed, cut them down. Think about purchasing a new inverter if the issue continues. My inverter says there is a grid loss failure; why is that? This may
