Solar energy is a powerful and renewable resource that harnesses sunlight to generate electricity and heat. This energy source is becoming increasingly popular as people look for cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels.
In this article, we’ll break down what solar energy is, its history, how it works, and the different types of solar energy systems available today. We’ll also explore the benefits of going solar and what the future holds for this sustainable energy source.
Key Takeaways
- Solar energy is derived from sunlight and can be converted into electricity or heat.
- Photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells.
- Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors to focus sunlight and generate heat.
- Solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning it won’t run out and is environmentally friendly.
- Investing in solar technology can significantly reduce energy costs and reliance on fossil fuels.
What Is Solar Energy?

So, what exactly is solar energy? Well, in simple terms, it’s energy that comes from the sun. This energy is harnessed in a few different ways to provide heat, electricity, and even power for cooking.
It’s a pretty big deal because it’s a renewable resource, meaning we’re not going to run out of it anytime soon (like, for another five billion years or so).
Solar energy can be used in a variety of ways. For example:
- Heating homes and buildings
- Generating electricity
- Heating water
- Powering vehicles
Solar energy is a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. It reduces our reliance on non-renewable resources and helps to lower our carbon footprint. Plus, it’s becoming more affordable and accessible all the time, making it a viable option for more and more people.
There are two main types of solar energy technologies:
- Active solar technologies: These use mechanical or electrical devices to convert sunlight into other forms of energy, like electricity or heat.
- Passive solar technologies: These take advantage of a building’s design and materials to naturally heat and cool the space, without using any external devices.
Solar energy is practical in areas with high amounts of sunlight and low cloud cover. Homes and businesses that install solar panels can even produce excess electricity and sell it back to the power grid, which can reduce or even eliminate power bills.
When Was Solar Power Discovered?
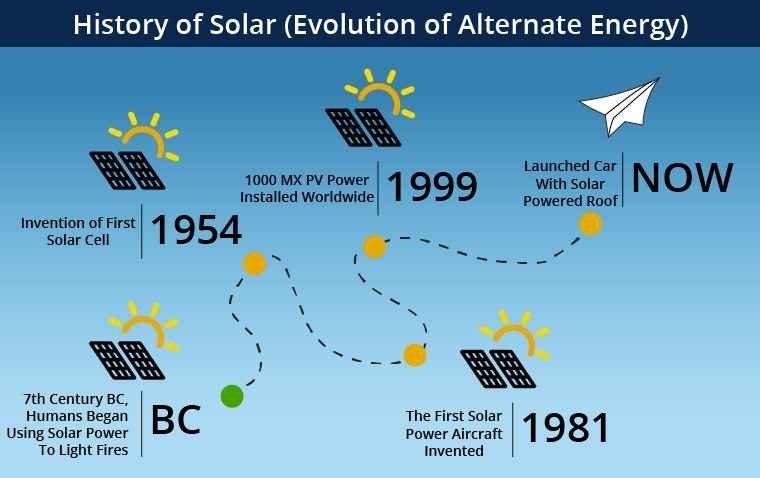
It’s interesting to think about how long we’ve known about solar power. It wasn’t some recent invention; the basic science goes way back. The story starts with some pretty cool discoveries that laid the groundwork for everything we use today.
The real breakthrough came in 1839 when Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, a French physicist, discovered the photovoltaic effect.
Basically, he found out that you could generate electricity by exposing certain materials to light. He was just 19 years old when he made this discovery!
Becquerel’s experiment involved silver-chloride in an acidic solution. When he shined light on it, platinum electrodes attached to the solution generated an electric current.
This was the first time someone had observed electricity being produced directly from sunlight, and it’s the foundation of how solar panels work today.
It’s amazing to think that a teenager’s experiment from almost two centuries ago is still relevant today. Becquerel’s discovery wasn’t immediately put to practical use, but it opened the door for future scientists and engineers to develop the solar technologies we rely on now.
While Becquerel’s discovery was a major step, it took many years for the technology to develop into something useful.
It wasn’t until the 20th century that solar cells became efficient enough to be practical. Still, his work is the starting point for understanding how we harness solar energy today.
Here’s a quick timeline:
- 1839: Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel discovers the photovoltaic effect.
- Late 19th Century: Scientists continue to study the photovoltaic effect, but practical applications are limited.
- 20th Century: Development of more efficient solar cells leads to practical applications, such as powering spacecraft.
Is Solar Energy Renewable?
So, is solar energy renewable? Absolutely! Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source because it comes from the sun, which is pretty much an endless supply of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form and are finite, the sun will keep shining for billions of years. That’s a long time!
Think about it this way:
- Fossil fuels are like a limited bank account. Once you spend all the money, it’s gone.
- Solar energy is like a paycheck that keeps coming in. As long as the sun is up, we can collect energy.
- Using solar energy helps reduce our reliance on those limited resources, like coal and oil.
Switching to renewable energy sources like solar is a big step towards a more sustainable future. It means less pollution, less environmental damage, and a more secure energy supply for everyone.
One of the coolest things about solar is that it’s clean. Once the solar panels are up and running, they don’t produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
This is a huge contrast to burning fossil fuels, which release all sorts of nasty stuff into the atmosphere. Plus, homes and businesses that install solar panels can even sell excess electricity back to the electric provider, reducing or even eliminating power bills.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
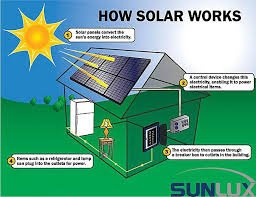
Solar energy is captured and converted into usable forms through various methods. These methods generally fall into two categories: active and passive.
Active solar technologies use electrical or mechanical devices to convert solar energy, while passive technologies leverage the local climate to heat or cool structures without external devices.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) modules, are the most common way to harness solar energy. They’re made up of numerous solar cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Each cell contains a semiconductor material, usually silicon. When sunlight strikes the cell, it knocks electrons loose from the silicon atoms.
These electrons are then forced to flow in one direction, creating an electric current. Metal contacts on the top and bottom of the cell collect this current, which can then be used to power electrical devices or sent to the grid. This process is called the photovoltaic effect.
How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity?
The process of generating electricity with solar panels involves several key steps:
- Sunlight hits the solar panel.
- Photons from the sunlight excite electrons in the semiconductor material.
- The excited electrons flow through an electrical circuit, creating electricity.
- This electricity is then collected and used to power homes, businesses, or other applications.
Solar panels are pretty amazing when you think about it. They quietly sit on your roof, soaking up the sun and turning it into electricity with no moving parts. It’s a clean, reliable way to generate power, and it’s becoming more and more affordable all the time.
How Does a Solar Panel System Work?
A complete solar panel system involves more than just the panels themselves. It includes several other components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electricity. Here’s a breakdown of how a typical system works:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
- Mounting System: Secures the solar panels to your roof or ground.
- Wiring: Connects all the components of the system.
- Monitoring System: Tracks the performance of the system and provides data on energy production.
What Does a Solar Inverter Do?
The solar inverter is a critical component of any solar panel system. Its primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity.
AC electricity is the standard form of electricity used in most homes and businesses. Without an inverter, the electricity generated by solar panels would not be compatible with most appliances and electrical devices.
Inverters also perform other important functions, such as monitoring the system’s performance and providing safety features like grid-tied inverters.
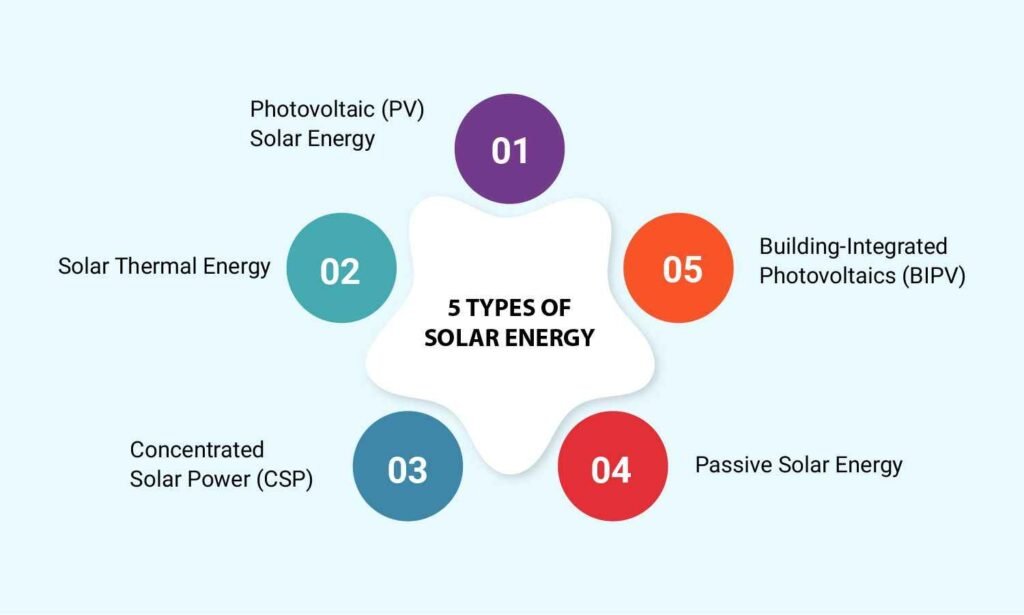
Types of Solar Energy
Solar energy systems come in a few different flavors, each with its own way of capturing and using the sun’s power. It’s not just about solar panels on roofs anymore; there are some pretty interesting technologies out there.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Power
This is probably what you think of first when you hear “solar energy.” Photovoltaic (PV) systems use solar cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are usually made of silicon and are grouped together to form solar panels.
- PV systems can be used for everything from powering small devices like calculators to providing electricity for entire cities.
- They’re relatively low-maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a popular choice for both residential and commercial use.
- The efficiency of PV cells has been steadily increasing over the years, making them an even more attractive option.
PV systems are a great way to reduce your carbon footprint and save money on your electricity bill. Plus, they’re a clean and renewable source of energy, which is good for the planet.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
Concentrated solar power (CSP) is a different approach. Instead of directly converting sunlight into electricity, CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to focus a large area of sunlight onto a small area.
This concentrated heat is then used to generate electricity, often by heating a fluid that drives a turbine. Concentrated solar energy can be used on a smaller scale, for instance, to generate heat for solar cookers.
- CSP plants can generate large amounts of electricity, making them suitable for utility-scale projects.
- Some CSP systems can store heat, allowing them to generate electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
- Different types of CSP technologies exist, including solar power towers, parabolic troughs, and Fresnel reflectors.
Passive Solar Energy
Passive solar energy is all about using the design of buildings and materials to capture and distribute solar energy for heating and cooling. It doesn’t involve any mechanical or electrical devices.
Instead, it relies on things like the orientation of the building, the size and placement of windows, and the use of materials that absorb and store heat. Homes and other buildings use passive solar energy to distribute heat efficiently and inexpensively.
- Passive solar design can significantly reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling, saving energy and money.
- It’s a cost-effective way to improve the energy efficiency of buildings.
- Effective passive solar design requires careful planning and consideration of the local climate.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels are the most visible part of any solar energy system. They’re responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity.
These panels are made up of many individual solar cells, typically made from silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it knocks electrons loose, creating an electrical current. The more sunlight, the more electricity generated. It’s pretty neat, actually.
How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity?
Okay, so we know sunlight hits the panels and creates electricity, but how does that actually happen? It’s all about the photovoltaic effect. When photons (light particles) strike the solar cells, they energize electrons in the silicon.
These energized electrons then flow through an electrical circuit, generating direct current (DC) electricity. Think of it like a tiny, sun-powered battery!
How Does a Solar Panel System Work?
Here’s where things get a little more complex. A solar panel system isn’t just one panel; it’s a whole setup working together. First, the solar panels capture sunlight and convert it to DC electricity.
Then, this DC electricity flows to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity – the kind that powers most homes and businesses.
From there, the AC electricity can be used to power your appliances, lights, and other electrical devices. Any excess electricity can be sent back to the grid, potentially earning you credits on your electricity bill.
What Does a Solar Inverter Do?
The inverter is a super important part of the system. Solar panels produce DC electricity, but our homes and the electrical grid use AC electricity.
The inverter’s job is to convert the DC electricity from the panels into usable AC electricity.
Modern inverters also do a lot more than just convert electricity. They monitor system performance, optimize energy production, and provide safety features. Without an inverter, your solar panels would be pretty useless for powering your home.
Think of the inverter as the translator between your solar panels and your home’s electrical system. It takes the language of DC electricity and turns it into the language of AC electricity, so everything can work together smoothly.
Where Is Solar Energy Used?

Solar energy is popping up everywhere these days, which is pretty cool. It’s not just some futuristic idea anymore; it’s actually being used in a bunch of different ways and places.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Power
PV solar power, which uses solar panels, is probably what most people think of when they hear “solar energy.” You see solar panels on rooftops all over the place, from houses in sunny California to office buildings in Germany.
These panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, which can then be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities. Satellites and the International Space Station also use PV solar power.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
CSP is a bit different. Instead of using solar panels, it uses mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver, which then heats a fluid to create steam.
This steam is then used to generate electricity in a turbine. CSP plants are often built in desert areas with lots of sunshine, like the Mojave Desert in the United States or parts of Spain and India. The Solar Energy Generating System (SEGS) in California is one example, generating a lot of electricity each year.
Passive Solar Energy
Passive solar energy is all about using the design of buildings to take advantage of sunlight for heating and cooling.
This can involve things like orienting a building to maximize sunlight exposure in the winter and minimize it in the summer, using materials that absorb and store heat, and designing windows and ventilation systems to promote natural airflow.
Passive solar design can be used in homes, schools, and other buildings to reduce energy consumption and improve comfort. It’s a really smart way to use the sun’s energy without needing any fancy equipment.
Solar cookers are another great example of where solar energy is used. These devices use mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a cooking surface, allowing people to cook food without using wood or other fuels.
Solar cookers are especially useful in developing countries, where they can help to reduce deforestation and improve air quality.
Here’s a quick rundown of where solar energy is making a difference:
- Residential homes: Powering lights, appliances, and heating/cooling systems.
- Commercial buildings: Reducing energy costs for businesses and organizations.
- Remote areas: Providing electricity to communities that are not connected to the grid.
- Agriculture: Powering irrigation systems and greenhouses.
- Transportation: Charging electric vehicles and powering public transportation systems.
Benefits of Solar Energy
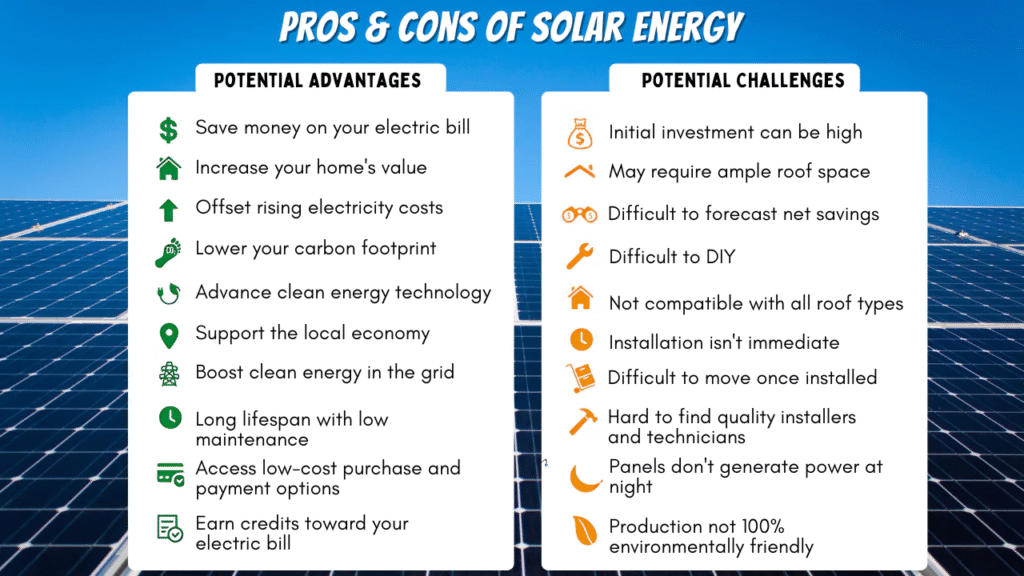
Solar energy is gaining popularity, and for good reason. It’s not just a fad; it offers some real, tangible advantages. Let’s break down some of the key benefits.
Environmentally Friendly
One of the biggest draws of solar power is its positive impact on the environment. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy doesn’t release harmful pollutants into the air or water.
It’s a clean energy source that helps reduce our carbon footprint. Think about it: no more contributing to smog or acid rain just to keep the lights on.
Plus, it helps conserve precious resources like coal and oil, which are finite. It’s a win-win for us and the planet. Using solar energy can drastically reduce the impact we have on the environment.
Off-Grid Living
Ever dreamed of living off the grid? Solar energy makes it a real possibility. With a properly sized solar panel system and battery storage, you can generate your own electricity and become independent from the traditional power grid.
This is especially appealing for people in rural areas where access to the grid might be limited or unreliable. Imagine the freedom of not being tied to a utility company and having control over your own energy supply.
Reduced Electricity Loss
Traditional power grids are prone to energy loss during transmission. Electricity has to travel long distances from power plants to homes and businesses, and some of it gets lost along the way. Solar energy, on the other hand, can be generated right where it’s needed – on your rooftop.
This reduces transmission losses and makes the energy system more efficient. It’s like having your own mini power plant, cutting out the middleman and keeping more energy in your pocket.
Enhanced Grid Security
A decentralized energy system, with solar power playing a key role, is more resilient to disruptions. If one part of the grid goes down, the rest can continue to function.
This is in contrast to a centralized system, where a single point of failure can cause widespread blackouts. Solar energy helps to diversify our energy sources and makes the grid more secure and reliable. It’s like having a backup plan in case of emergencies.
Free Source of Energy
Once you’ve invested in a solar panel system, the sun’s energy is free for the taking. You’re no longer subject to the fluctuating prices of fossil fuels.
This can lead to significant cost savings over the long term. Think of it as an investment that pays for itself over time, providing you with clean, free energy for years to come.
Switching to solar energy is a long-term investment that not only benefits the environment but also provides financial security and independence. It’s a step towards a more sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.
Why Go Solar?

Switching to solar energy is a big decision, but it’s one that more and more people are making every day. It’s not just about being trendy; there are some solid reasons to consider it. Let’s break down why you might want to make the leap.
One of the biggest reasons people go solar is to save money. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term savings can be substantial.
Think about it: no more (or at least, way smaller) electricity bills. Plus, in some areas, you can even sell excess energy back to the grid. That’s like getting paid to use the sun!
Another huge factor is the environment. Solar energy is clean and renewable. It doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or air pollution like fossil fuels do. By going solar, you’re reducing your carbon footprint and helping to protect the planet. It’s a win-win.
Here’s a quick rundown of some key benefits:
- Lower electricity bills
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Increased home value
- Energy independence
Making the switch to solar is a commitment to a more sustainable future. It’s about taking control of your energy consumption and making a positive impact on the world around you. It’s not always the easiest path, but it’s definitely one worth considering.
Finally, there’s the aspect of energy independence. With solar panels, you’re less reliant on the traditional power grid.
This can be especially appealing if you live in an area with frequent power outages. Plus, it just feels good to be more self-sufficient. You can even use solar energy for various applications, including solar water heaters.
History of Solar Energy
Solar energy’s story is a long one, stretching back centuries. It’s not a newfangled invention; people have been figuring out ways to use the sun’s power for a very long time.
From simple applications to the complex tech we have today, it’s been quite a journey. It’s interesting to see how our understanding and use of solar energy has evolved.
Early uses were pretty basic, like using the sun to dry food or heat homes. It wasn’t until much later that we started to understand the science behind it and develop technologies to really harness its potential.
Here’s a quick look at some key moments:
- Early Days: Ancient civilizations used sunlight for heating spaces.
- 1800s: Scientists started discovering the science behind the photovoltaic effect.
- 1950s: The first solar cells were developed, though they were expensive and not very efficient.
- Today: Solar energy is becoming more affordable and widespread, with advancements happening all the time.
Future of Solar Energy
Solar energy is already making a big splash, but what’s next? Well, a lot of smart people are working on making it even better, cheaper, and more accessible. It’s not just about putting panels on roofs anymore; it’s about integrating solar into everything.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Power
PV tech is getting a serious upgrade. Think more efficient solar cells that can grab more sunlight, even on cloudy days.
We’re talking about stuff like perovskite solar cells, which could seriously change the game because they’re cheaper to make and potentially way more efficient than the silicon ones we use now.
Plus, they’re working on flexible solar panels that you could stick on pretty much anything. Imagine your backpack charging your phone while you hike!
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
CSP plants are also getting a makeover. They’re trying out new ways to store the heat they collect, so they can keep making electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
This is a big deal because it means CSP could become a reliable, 24/7 power source, not just something that works during the day. This could make CSP a real contender for replacing fossil fuel power plants.
Passive Solar Energy
Passive solar is getting smarter too. Architects are using new materials and designs to build homes and buildings that naturally stay warm in the winter and cool in the summer, all without needing a ton of extra energy.
It’s all about using the sun’s energy in a clever way to cut down on energy bills and reduce our carbon footprint.
Solar energy is poised for massive growth. Innovations in materials, energy storage, and grid integration will make solar power an even more important part of our energy mix. The push for sustainable solutions is driving investment and research, promising a brighter, cleaner future powered by the sun.
Here’s a quick look at some future trends:
- Improved Energy Storage: Batteries are getting better and cheaper, making it easier to store solar energy for when you need it.
- Smart Grids: Upgrading our power grids to handle more solar energy and distribute it efficiently.
- Solar-Powered Transportation: More electric cars, buses, and even planes powered by solar energy.
What is solar energy in simple words?
Solar energy is power we get from the sun’s light.
Solar panels collect sunlight and turn it into electricity.
It’s clean, renewable, and doesn’t pollute the air.
Basically, it’s a way to use sunshine to run things like lights, TVs, and even your whole house — for free.
What are 5 advantages of solar energy?
- It’s 100% renewable.
- Saves money on electricity bills.
- Low maintenance once installed.
- Good for the environment (no emissions).
- Can increase your home’s value.
Solar energy also gives you energy independence — you’re not tied to big utility companies forever.
How is solar energy used?
Solar energy is used to power homes, businesses, and even satellites.
It can heat water, charge batteries, and run appliances.
Some farms use it to pump water.
It’s also used in street lighting and solar-powered gadgets.
Pretty much anything that uses electricity can run on solar power.
Why is solar power the best energy source?
Solar power is the best because it’s free, clean, and never runs out.
Unlike fossil fuels, it doesn’t pollute or damage the planet.
It lowers energy bills, helps fight climate change, and works almost anywhere.
Plus, it’s super quiet and low maintenance.


